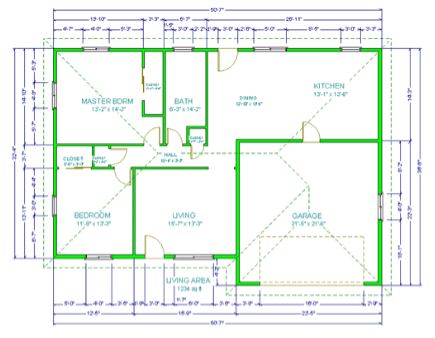
CIVIL CAD
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computer systems to assist in the
creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. CAD software is used
to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve
communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing.
CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other
manufacturing operations.
DRAFTING
Technical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is
the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something
functions or is to be constructed.
Technical drawing is essential for communicating ideas in industry and engineering.
To make the drawings easier to understand, people use familiar symbols, perspectives,
units of measurement, notation systems, visual styles, and page layout. Together,
such conventions constitute a visual language, and help to ensure that the drawing
is unambiguous and relatively easy to understand.
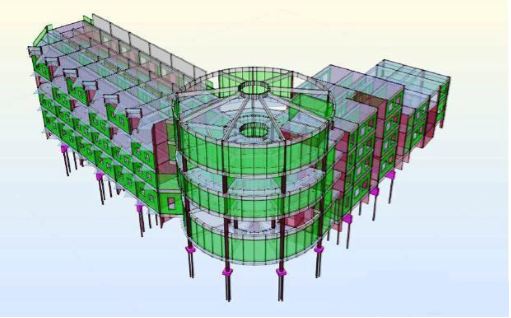
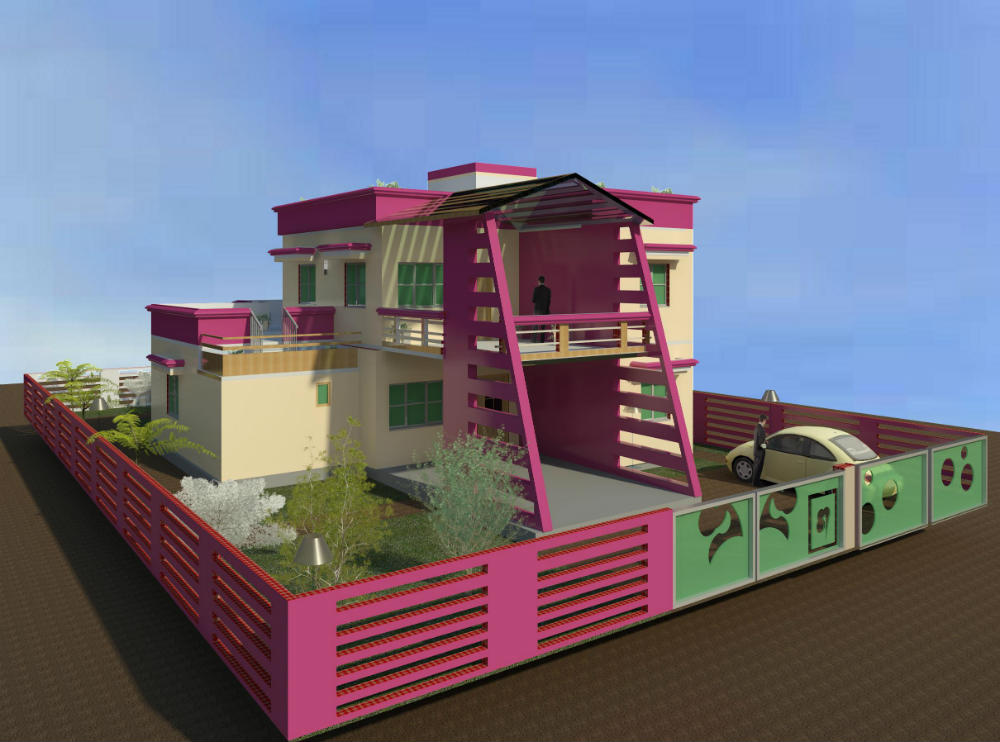
MODELING
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a process involving the generation
and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics
of places. Building information models (BIMs) are files which can be exchanged or
networked to support decision-making about a place. Current BIM software is used
by individuals, businesses and government agencies who plan, design, construct,
operate and maintain diverse physical infrastructures, from water, wastewater, electricity,
gas, refuse and communication utilities to roads, bridges and ports, from houses,
apartments, schools and shops to offices, factories, warehouses and prisons, etc.
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a digital representation of physical and
functional characteristics of a facility. A BIM is a shared knowledge resource for
information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life-cycle;
defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition.

STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
A structure refers to a body or system of connected parts used to support a load.
In Civil Engineering, structure includes buildings, bridges, and towers.
Structural Analysis is defined as an Examination of the different components or
elements that make up an organization or system, to discover their interrelationships
and relative importance in the realization of its goals or purpose. It is the determination
of the effects of loads on physical structures and their components.
Structural analysis incorporates the fields of applied mechanics, materials science
and applied mathematics to compute a structure's deformations, internal forces,
stresses, support reactions, accelerations, and stability.
The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure's fitness for use, often
saving physical tests. Structural analysis is thus a key part of the engineering
design of structures.